Why Is the Protist Kingdom Said to Be Diverse Clip Art of Mushroom
Table of Contents
What is Fungi?
Construction of Fungi
Characteristics of Fungi
Classification of Fungi
Reproduction in Fungi
Uses of Fungi
Examples of Fungi

What is Fungi?
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms that include microorganisms such as yeasts, moulds and mushrooms. These organisms are classified under kingdom fungi.
The organisms found in Kingdom fungi contain a cell wall and are omnipresent. They are classified equally heterotrophs among the living organisms.

Kingdom Fungi
To proper noun a few – the appearance of blackness spots on staff of life left outside for some days, the mushrooms and the yeast cells, which are commonly used for the product of beer and bread are likewise fungi. They are besides establish in most of the skin infections and other fungal diseases.
If we observe carefully, all the examples that nosotros cited involve moist conditions. Thus, we can say that fungi commonly grow in places which are moist and warm enough to support them.
Allow the states have a detailed overview of the structure, classification and characteristics of fungi.
Also Read:Kingdom Animalia
Structure of Fungi
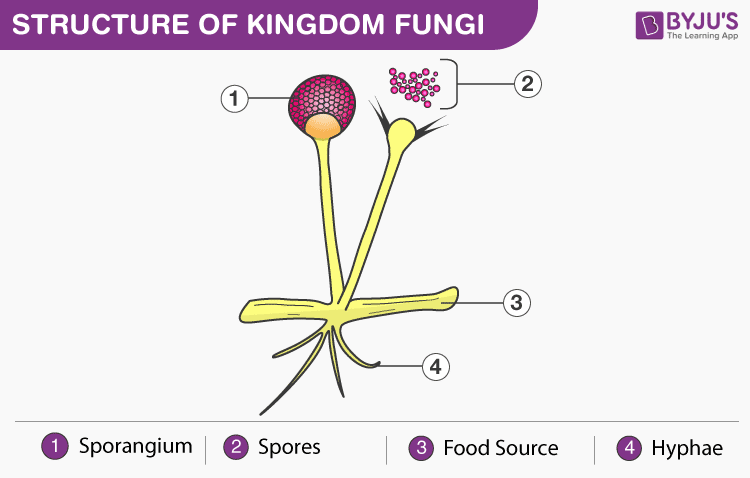
Structure of Fungi
The structure of fungi can be explained in the following points:
- Almost all the fungi have a filamentous structure except the yeast cells.
- They can be either unmarried-celled or multicellular organism.
- Fungi consist of long thread-like structures known as hyphae. These hyphae together form a mesh-similar structure called mycelium.
- Fungi possess a prison cell wall which is made upwards of chitin and polysaccharides.
- The cell wall comprises protoplast which is differentiated into other cell parts such as cell membrane, cytoplasm, jail cell organelles and nuclei.
- The nucleus is dense, clear, with chromatin threads. The nucleus is surrounded by a nuclear membrane.
Besides Refer: Fungal Prison cell Wall
Characteristics of Fungi
Following are the of import characteristics of fungi:
- Fungi are eukaryotic, non-vascular, non-motile and heterotrophic organisms.
- They may be unicellular or filamentous.
- They reproduce by means of spores.
- Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation.
- Fungi lack chlorophyll and hence cannot perform photosynthesis.
- Fungi shop their food in the form of starch.
- Biosynthesis of chitin occurs in fungi.
- The nuclei of the fungi are very modest.
- The fungi have no embryonic stage. They develop from the spores.
- The mode of reproduction is sexual or asexual.
- Some fungi are parasitic and tin infect the host.
- Fungi produce a chemical called pheromone which leads to sexual reproduction in fungi.
- Examples include mushrooms, moulds, yeast.
Also Read:V Kingdom Classification
Classification of Fungi
Kingdom Fungi are classified based on dissimilar modes. The different nomenclature of fungi is as follows:
Based on Way of nutrition
On the footing of nutrition, kingdom fungi can be classified into three groups.
- Saprophytic – The fungi obtain their nutrition past feeding on expressionless organic substances. Examples: Rhizopus, Penicillium and Aspergillus.
- Parasitic – The fungi obtain their nutrition by living on other living organisms (plants or animals) and absorb nutrients from their host. Examples: Taphrina and Puccinia.
- Symbiotic – These fungi live byhavinganinterdependent relationship association with other species in which both are mutually benefited. Examples: Lichens and mycorrhiza. Lichens are the symbiotic association betwixt algae and fungi. Here both algae and fungi are mutually benefited as fungi provide shelter for algae and in reverse algae synthesis carbohydrates for fungi.
Based on Spore Formation
Kingdom Fungi are classified into the following based on the formation of spores:
- Zygomycetes – These are formed by the fusion of two different cells. The sexual spores are known as zygospores while the asexual spores are known as sporangiospores. The hyphae are without the septa.
- Ascomycetes – They are too called as sac fungi. They can be coprophilous, decomposers, parasitic or saprophytic. The sexual spores are chosen ascospores. Asexual reproduction occurs past conidiospores. Instance – Saccharomyces
- Basidiomycetes – Mushrooms are the well-nigh commonly found basidiomycetes and mostly live as parasites. Sexual reproduction occurs by basidiospores. Asexual reproduction occurs by conidia, budding or fragmentation. Instance- Agaricus
- Deuteromycetes – They are otherwise called imperfect fungi as they exercise not follow the regular reproduction wheel as the other fungi. They do not reproduce sexually. Asexual reproduction occurs by conidia. Example – Trichoderma.
As well Read: Difference Between Algae And Fungi
Reproduction in Fungi
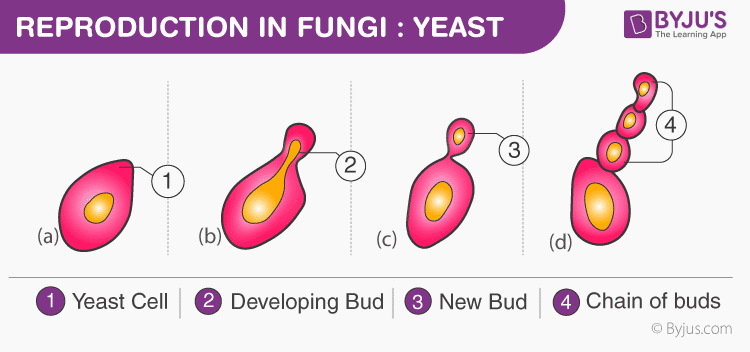
Reproduction in Fungi
Reproduction in fungi is both by sexual and asexual means. The sexual manner of reproduction is referred to every bit teleomorph and the asexual way of reproduction is referred to as anamorph.
Vegetative reproduction – By budding, fission and fragmentation
Asexual reproduction – This takes identify with the help of spores chosen conidia or zoospores or sporangiospores
Sexual reproduction – ascospores, basidiospores, and oospores
The conventional mode of sexual reproduction is not always observed in the kingdom Fungi. In some fungi, the fusion of two haploid hyphae does not upshot in the formation of a diploid jail cell. In such cases, there appears an intermediate stage chosen the dikaryophase. This stage is followed by the germination of diploid cells.
As well Read:Kingdom Monera, Protista and Fungi
Recommended Video:

Uses of Fungi
Fungi are i of the most important groups of organisms on the planet every bit information technology plays a vital role in the biosphere and has great economic importance on account of their both benefits and harmful effects.
Following are some of the important uses of fungi:
- Recycling– They play a major part in recycling the dead and decayed affair.
- Nutrient– Mushrooms species are edible which are cultured and are used as food by humans.
- Medicines– There are many fungi which are used to produce antibiotics, to control diseases in humans and animals. Penicillin antibiotic is derived from a common fungi Penicillium.
- Biocontrol Agents – Fungi are involved in exploiting insects, other small-scale worms and help in controlling pests. Spores of fungi are used equally spray-on crops.
- Food spoilage – Fungi play a major role in recycling organic cloth and are also responsible for major spoilage and economic losses of stored food.
Examples of Fungi
Following are the common examples of fungi:
- Yeast
- Mushrooms
- Moulds
- Truffles
Also Read:Plant Kingdom
To know more about what is fungi, its structure, characteristics of fungi, nomenclature of fungi, different examples of fungi and other concepts related to kingdom fungi, keep visiting BYJU'S website or download the BYJU'S app for further reference.
Oftentimes Asked Questions on Fungi
Which organisms belong to kingdom fungi?
Kingdom fungi include mushrooms, yeast, moulds containing filamentous structures chosen hyphae.
What are the different types of fungi?
The unlike types of fungi include- Zygomycetes Basidiomycetes, Ascomycetes, and Deuteromycetes.
Which kingdom is closely related to kingdom fungi?
Kingdom fungi are closely related to the animal kingdom. This has been determined past phylogenetic studies. The phylogenetic tree explains how animals diverged from fungi millions of years ago.
What is common between plants and fungi?
Plants and fungi, both have a cell wall.
Which form of kingdom fungi can motion?
Chytridiomycota produces flagellated gametes and is the merely exception to the group that can move with the help of flagella. These are ancient fungi and are believed to be a connecting link between fungi and animals.
Source: https://byjus.com/biology/kingdom-fungi/
0 Response to "Why Is the Protist Kingdom Said to Be Diverse Clip Art of Mushroom"
Post a Comment